从一个带并发数限制的请求深入 Dart 的 Future
#Dart
字数统计:19k 字
阅读时长 ≈ 17 分钟
在项目开发中,我们经常需要同时请求多个接口。为了提升效率,通常会采用并发请求 的方式。这是一个非常经典的异步编程场景。
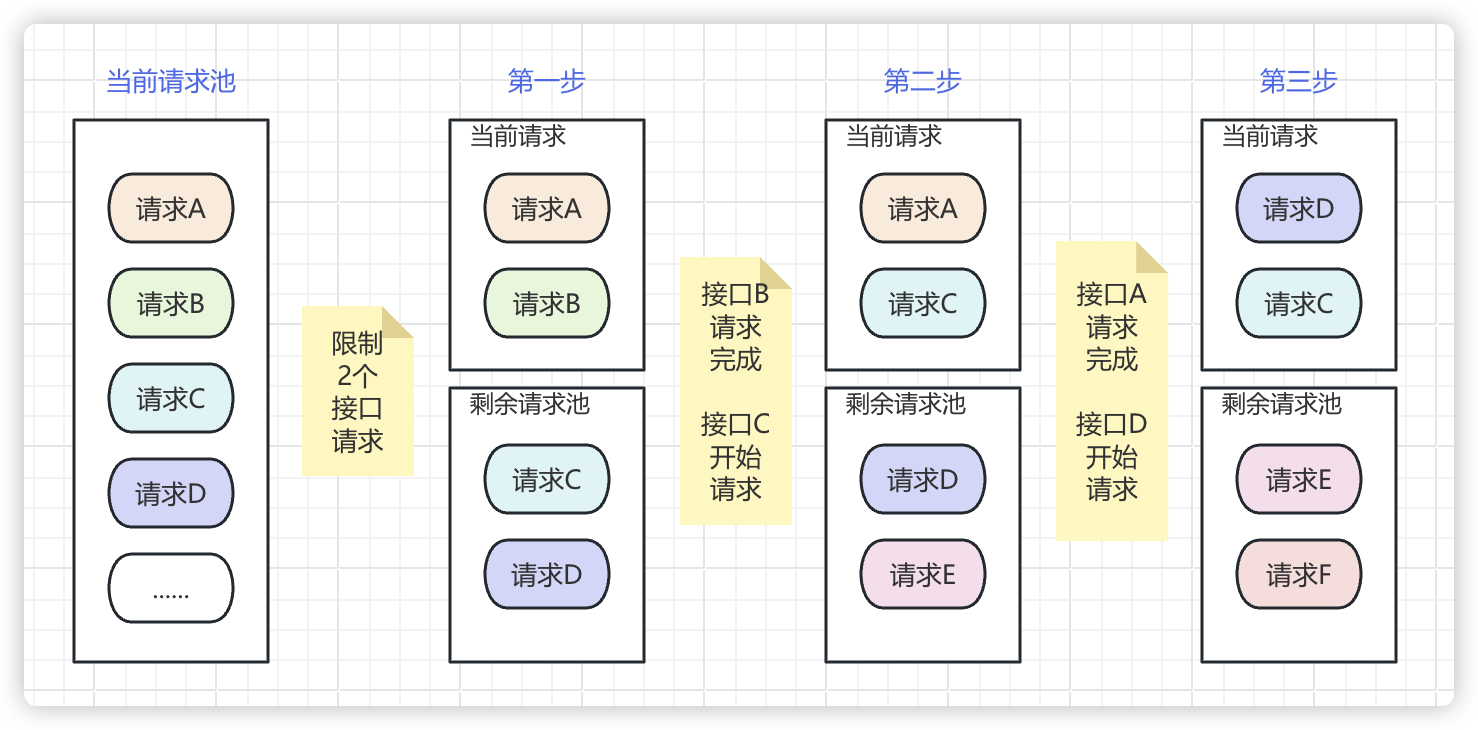
下图直观地展示了这一过程:
然而,无限制地并发请求可能带来性能问题(如内存溢出、服务器压力过大等)。因此,限制最大并发数成为一种常见的优化策略。而要实现这一需求,离不开对 Dart 中 Future 和 Completer 的深入理解。
Future:异步操作的核心 什么是 Future Future 是一个表示异步操作最终结果的对象。它代表一个未来某个时刻才会可用的值(或错误)。
核心特性
异步非阻塞:不会阻塞主线程;
单次完成:一个 Future 只能完成一次(成功或失败);
链式调用:支持 .then()、.catchError()、.whenComplete() 等方法;
三种状态
Uncompleted(未完成)Completed with data(成功)Completed with error(失败)
基本用法示例 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 Future<String > fetchList() async { final res = await http.get ('...' ); return res.body; } void main() { fetchList().then((_) { print ('success' ); }).catchError((e) { print ('error: $e ' ); }).whenComplete(() { print ('complete' ); }); Future.delayed(Duration (seconds: 1 ), () { print ('delayed task done' ); }); print ('main done' ); }
使用 async/await 是构建 Future 最常见的方式;
Future.delayed 可创建延迟执行的任务;还有 Future.wait(等待所有),Future.any (任意完成即返回) 等实用工具;
实现带并发限制的请求队列 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 Future<void > fetchQueue( List <Future<dynamic >> queueTask, int max, Function (List <dynamic >) callback, ) async { final result = List <dynamic >.filled(queueTask.length, null ); int runningTask = 0 ; int nextIndex = 0 ; int completedCount = 0 ; void runNext() { while (runningTask < max && nextIndex < queueTask.length) { final task = queueTask[nextIndex]; final currentIndex = nextIndex; nextIndex++; runningTask++; task .then((value) { result[currentIndex] = value; }) .catchError((error) { result[currentIndex] = error; }) .whenComplete(() { runningTask--; completedCount++; runNext(); if (completedCount == queueTask.length) { callback(result); } }); } } runNext(); if (queueTask.isEmpty) { callback([]); } }
这种方式通过递归调度控制并发数,逻辑清晰,但依赖外部回调,不够“Future-native”。
Completer:手动控制 Future 的完成 什么是 Completer Completer 是一个手动完成 Future 的控制器。它允许你在任意时机(通常在回调函数中)显式地完成(成功或失败)一个 Future。
为什么需要它?
当异步逻辑无法用 async/await 直接表达时(如桥接回调 API);
需要精确控制 Future 的完成时机;
构建更复杂的异步流程(如超时、重试、并发调度等)。
核心特性
手动完成:不像 async 函数自动完成;
单次完成:重复调用 complete() 会抛出 StateError;
状态可查:通过 completer.isCompleted 判断;
一对一绑定:每个 Completer 对应一个 Future,但该 Future 可被多处监听。
基本用法示例 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 Future<String > callNativeMethod(String method, dynamic arguments) { final completer = Completer<String >(); methodChannel .invokeMethod(method, arguments) .then((result) { completer.complete(result.toString()); }) .catchError((error) { completer.completeError(error); }); return completer.future; }
completer.complete(value):成功完成;completer.completeError(error):失败完成;completer.future:获取关联的 Future。
用 Completer 重构并发请求队列 现在,我们用 Completer 将上述逻辑改造成返回 Future 的函数 ,更符合 Dart 的异步风格:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 Future<List <dynamic >> fetchQueue( List <Future<dynamic >> tasks, int maxConcurrent, ) async { if (tasks.isEmpty) return []; final results = List <dynamic >.filled(tasks.length, null ); final completer = Completer<List <dynamic >>(); int running = 0 ; int nextIndex = 0 ; int completed = 0 ; void runTask() { if (nextIndex >= tasks.length) return ; final index = nextIndex++; final task = tasks[index]; running++; task .then((value) => results[index] = value) .catchError((error) => results[index] = error) .whenComplete(() { running--; completed++; if (nextIndex < tasks.length) { runTask(); } if (completed == tasks.length) { completer.complete(results); } }); } for (int i = 0 ; i < maxConcurrent && nextIndex < tasks.length; i++) { runTask(); } return completer.future; }
使用方式
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 final futureList = [ http.get ('url1' ), http.get ('url2' ), ]; final results = await fetchQueue(futureList, 3 ); print (results);
返回一个标准的 Future<List>,便于组合;
内部使用 Completer 精确控制完成时机;
支持错误捕获并保留在结果数组中(便于后续处理)。
总结
Future 是 Dart 异步编程的基石,代表一个未来值;Completer 提供了对 Future 完成过程的手动控制能力,适用于复杂异步场景;在实现带并发限制的请求队列时,Completer 能让我们写出更清晰、更“Dart 风格”的代码;
实际项目中,也可借助 package:stream_channel 或 package:async 中的 StreamGroup、CancelableOperation 等高级工具进一步简化逻辑。